Social Engineering
Social engineering attacks include phishing, spear-phishing, CEO Fraud, Ransomware and so much more. Learn about different attack methods used by the cyber criminals and how you can manage this ongoing problem and mitigate the risk.
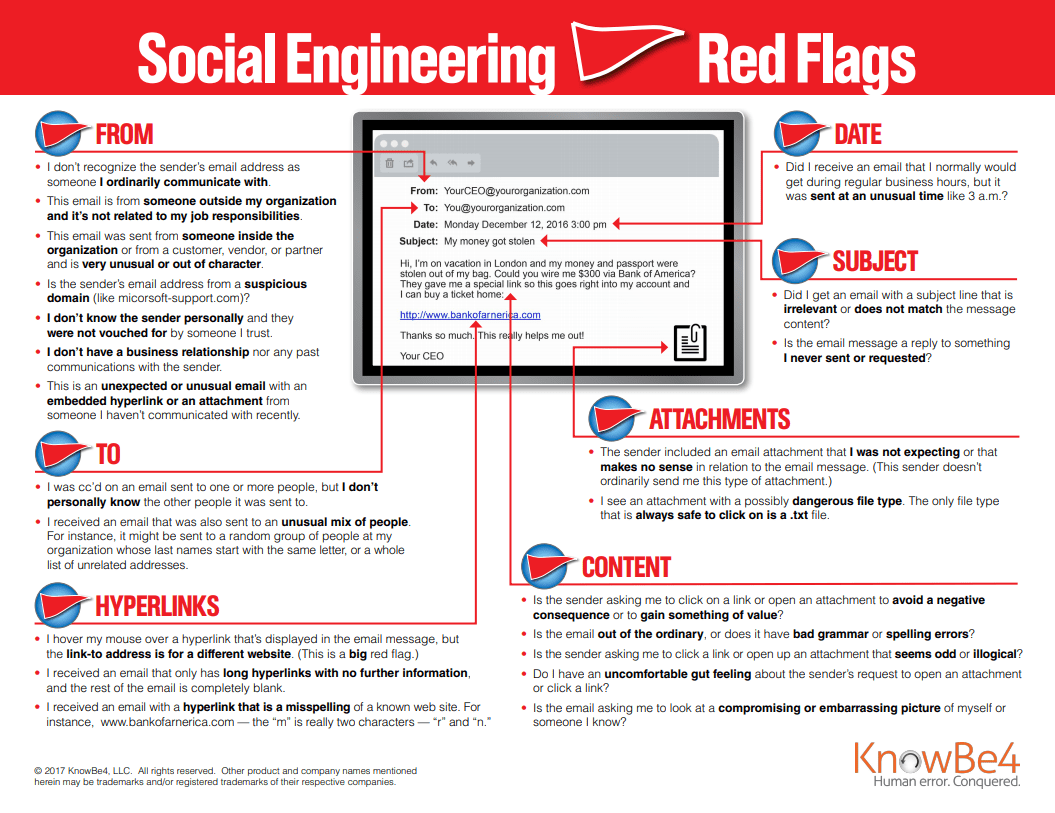
What is Social Engineering?
Social engineering is the art of manipulating, influencing, or deceiving you in order to gain control over your computer system. The hacker might use the phone, email, snail mail or direct contact to gain illegal access. Phishing, spear phishing, and CEO Fraud are all examples.
Social Engineer
So, who are these people? It could be a hacker in the USA who is out to do damage or disrupt. It could be a member of an Eastern Europe cyber crime mafia that is trying to penetrate your network and steal cash from your online bank account. Or, it could be a Chinese hacker that is trying to get in your organisation’s network for corporate espionage.
Ask Me Anything with Kevin Mitnick on Social Engineering
KnowBe4's Chief Hacking Officer, Kevin Mitnick, sat down with our team for an exclusive interview where we could ask him anything. We thought you’d like to hear his answers, too. Ever wonder what he thinks about social engineering and pen testing, how he got into the business, why he works with KnowBe4? Find out now, it's 7 minutes well spent!
Top 10 Techniques Used by Social Engineers
Phishing
The process of attempting to acquire sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details by masquerading as a trustworthy entity using bulk email which tries to evade spam filters. Emails claiming to be from popular social web sites, banks, auction sites, or IT administrators are commonly used to lure the unsuspecting public. It’s a form of criminally fraudulent social engineering. Also see Spear Phishing.
Spear-Phishing
A small, focused, targeted attack via email on a particular person or organisation with the goal to penetrate their defences. The spear phishing attack is done after research on the target and has a specific personalised component designed to make the target do something against their own interest. Here is more about how they do it.
Pretexting
This was the method used in the recent Twitter breach.
Diversion Theft
Baiting
Rogue
Quid Pro Quo
Honeytrap
Tailgating
Water-Holing
Did you know that 77% of successful social engineering attacks started with a phishing email?
How many of your users will take the bait and reply to a spoofed email?
Did you know that 60% of spoofed email attacks do not include a malicious link or attachment? KnowBe4's new Phishing Reply Test makes it easy for you to check to see if key users in your organisation will reply to a highly targeted social engineering attack, before the bad guys do.
10 Ways To Make Your Organisation A Hard Target
- With any ransomware infection, nuke the infected machine from orbit and re-image from bare metal.
- Get Secure Email Gateway and Web Gateways that cover URL filtering and make sure they are tuned correctly.
- Make sure your endpoints are patched religiously, OS and 3rd Party Apps.
- Make sure your endpoints and web gateway have next-gen, frequently updated (a few hours or shorter) security layers, but don’t rely on them alone.
- Identify users that handle sensitive information and enforce multi-factor authentication for them on absolutely everything, business & personal.
- Regularly review your internal security policies and procedures, specifically related to financial transactions to prevent CEO fraud. Have a two-tier payment authorisation process.
- Check your firewall configuration and make sure no criminal network traffic is allowed out to C&C (Command & Control) servers.
- Leverage new-school security awareness training, which includes frequent social engineering tests using multiple channels, not just email.
- You need to have weapons-grade backups in place that are regularly tested.
- Work on your security budget to show it is increasingly based on measurable risk reduction, and try to eliminate overspending on point-solutions targeted at one threat-or-another.